BPM Analytics
Advances in Technology in Relation to Learning Models in Healthcare
Artificial intelligence (AI) can boost the quality and delivery of healthcare worldwide. It can improve patient care, treatment outcomes, and most importantly, access to high quality healthcare. Over time, the efficiency and productivity of the healthcare systems can be honed to perform at higher levels of precision so that healthcare professionals are able to spend more time in direct patient care. It will also boost the speed at which life-saving treatments reach the market. Many countries are investing in AI-related healthcare research. It is one of the most prominent healthcare sectors being studied by governments and private businesses.
The healthcare sector generates massive amounts of complex data, that too at a very fast pace. Data is generated at hospitals and any healthcare providing facility, and also in areas related to medical insurance, medical equipment and medical research. Artificial intelligence (AI), advanced analytics and machine learning (ML) have all made it possible to transform big data into meaningful and actionable intelligence that can help boost healthcare quality and delivery, support decision-making and help overall improvement of processes and services.
Existing and possible future uses of AI in healthcare
Diagnostics:
-
Medical images:
-
Outcome analysis:
Surgical workflow:
-
Telemedicine:
Home care:
Drug development:
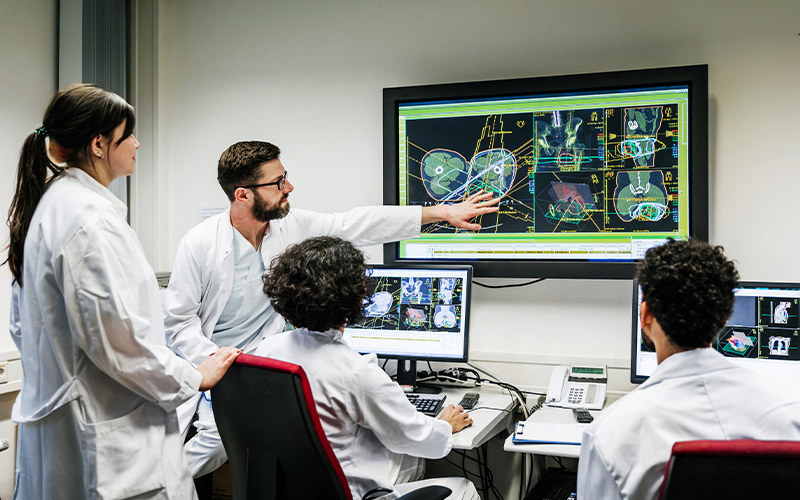
Radiology, pathology and ophthalmology are all benefited by AI. Time-consuming tasks can be automated, and diagnostics can be continuously improved, including early detection of health issues. AI-advanced microscopes can scan and detect dangerous blood diseases. Early detection of cancer is a reality because of AI-powered screenings.
An important example of AI is the analysis of patient scans. AI can extract important information from images, starting with the type of image and the body part being studied, followed by detection of any anomalies. AI algorithms can be trained to detect even the tiniest of anomalies in the deep brain, one of the most difficult areas for humans to reach.
Mining patient data to understand outcomes is already a common practice. AI tools are used to compare and analyse treatment outcomes of many patients and, thereby, establish trends. Such information is then used to recommend treatment paths for patients with the same or related disease. Having the right information could also help doctors identify risk markers and intervene at the right time. It also allows doctors to take a predictive approach rather than one of trial-and-error.
Videos and other sensor data can be analysed dynamically to understand progress and condition of a procedure in real time. The information can be used for retrospective analysis both in academics and patient care. Statistical evaluation of OR activities can also be analysed with this data. AI-powered surgical robots are already a reality.
Certain ML companies are exploring ways to provide doctors with relevant information during telemedicine sessions. The process will include capturing data during the session to help increase efficiency.
Use of AI solutions can support a shift from hospital to home-based care as patients take increased ownership of their care. Services that could be supported by AI solutions include remote monitoring and alerting systems or virtual assistants. Advances are already being made along these lines in neurology and nephrology; gradually, oncology and cardiology may be brought into the fold. Deploying AI in these areas will require inclusion of NLP, advances in deep learning, connectivity, capacity and quite an extensive change in culture and mindset.
Pharmaceutical companies are using ML to analyse many questions. A possible area is predicting how patients would respond to a drug, and which patients stand to gain from the drug.
Future of AI in healthcare
While it is almost impossible to predict exactly what the future holds for AI, it is clear that with medical data becoming more and more standardised and digitised, large pools of international data will be easily available. This means that an expanding number of tasks will be automated, increasing the versatility and precision of such systems. AI algorithms are continuously evolving, and with increasing amounts of data to tap into, the analysis is expected to become better and better, making healthcare providers more sentient and hyper-productive.*
However, there are pitfalls. Factors that need to be addressed are quality of the data used, ease of using AI, the quality of the algorithms, and the need for multidisciplinary development. Healthcare staff also need to be involved in the process for acceptance and success of the efforts.
Lastly, it has become essential to tackle the ethical questions raised about the potential risks of harnessing such vast amounts of healthcare data. The fine line between how much data is owned by healthcare facilities and how much by patients would require deep thought and compassion.
* For organizations on the digital transformation journey, agility is key in responding to a rapidly changing technology and business landscape. Now more than ever, it is crucial to deliver and exceed on organizational expectations with a robust digital mindset backed by innovation. Enabling businesses to sense, learn, respond, and evolve like a living organism, will be imperative for business excellence going forward. A comprehensive, yet modular suite of services is doing exactly that. Equipping organizations with intuitive decision-making automatically at scale, actionable insights based on real-time solutions, anytime/anywhere experience, and in-depth data visibility across functions leading to hyper-productivity, Live Enterprise is building connected organizations that are innovating collaboratively for the future.