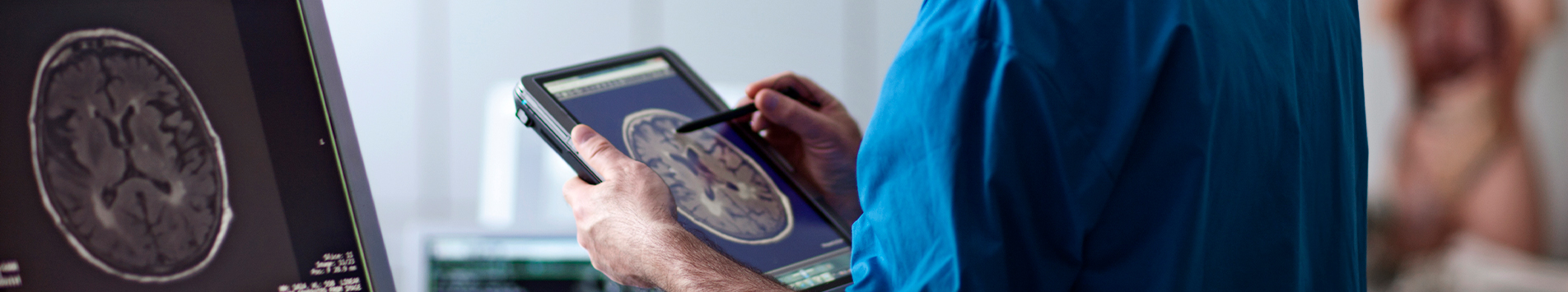
During the peak of the Covid pandemic, one health parameter that was at the centre of attention was the oxygen level in blood. The monitoring of this parameter was crucial to monitor critical changes in patients’ conditions. The scramble for beds and shortage of oxygen cylinders made it an extremely difficult time for the healthcare industry. There were many cases where the oxygen cylinders were taken by people who may not have required it and those needing it were left stranded. Imagine if there had been a system to collect continuous and real-time data on those important parameters of patients, it could have led to better utilisation of resources and more lives could have been saved. That system is steadily becoming reality.
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) refers to a group of technology-enabled devices that can capture specific physiological parameters from patients and relay them in real time to applications/platforms that can collect, collate, and process that data for healthcare professionals. This can be done even when the patient is outside of any kind of clinical setting. Some commonplace examples of RPM usage include -
- Blood Glucose levels in diabetics
- Blood pressure and heart rate monitoring
- Pulse rate, body temperature
- Oxygen levels in blood, respiratory rates
- Surveillance for patients with mental illness, differently-abled patients
- Substance abuse rehabilitation
The Technology and Scope of RPM
The four main processes that are at the core of any RPM are data collection, data relay to specific applications/platforms, data storage and security, and data analysis and implementation.
Data Collection – The parameters can be collected either automatically, continuously, or with user inputs through any of the RPM devices. The monitoring devices available include Bluetooth which can transmit health data via the internet to the healthcare team, wearable devices like watches, embedded biosensors, surveillance monitors, handheld medical devices, and even mobiles with specific applications.
Data Relay – The data is then stored in hospital databases and can be accessed from anywhere via a cloud repository and shared with doctors. One example of an RPM system that uses both the internet and GSM (Global System for Mobile communication) is aptly called Virtual Eye (VI). The VI can send a text message to the mobile of designated personnel to monitor patient status.
Data Security – Caution must be exercised while handling patient records and data. Personal health records are governed by privacy laws and hence proper encryptions and data security measures are imperative during the digital movement and storage of data.
Data Analysis and Implementation – Big data analytics are indispensable to the flood of data generated by RPM systems. Predictive analytics stems from this and is an emerging technology attracting investments to the tune of 260 million USD annually according to a 2019 report from Frost & Sullivan.
Once the data is analysed by the system and personnel, the specific medical advisories must be relayed back to user platforms for appropriate actions. This would then complete the loop. One instance would be a text message delivered to the primary caregiver to hospitalise the patient in case of fluctuating sugar or blood pressure levels.
While RPM is currently catering to patient categories like chronic illnesses, post-discharge long-term monitoring, and senior care, it is just a matter of time before it is found useful and feasible for others too.
Benefits and Beyond
Some of the advantages of remote patient monitoring are as follows. It allows patients (especially ones who are aged and/or getting treated for chronic illnesses) to be treated in the comfort of their homes. It reduces the risk of hospital infections and saves time on travel without compromising the quality of health care received. It can forewarn the primary caregivers and family in case of deterioration or alarming parameters. RPM also has scope for personalisation. It allows patients to have access to their health data for future reference and review. RPM has been used in a lot of long-drawn cancer treatments which need out-patients to be monitored on multiple parameters. The use of RPM can also result in operational efficiencies for healthcare professionals. For example, the number of non-emergency visits can be reduced resulting in savings of time, effort, and costs while also addressing the problem of medical equipment shortages to a certain extent. RPM systems have evolved as an extended arm of the medical community and have given the medical community greater access to health data and a deeper reach to the patient community outside the purview of traditional clinical settings.
* For organizations on the digital transformation journey, agility is key in responding to a rapidly changing technology and business landscape. Now more than ever, it is crucial to deliver and exceed organizational expectations with a robust digital mindset backed by innovation. Enabling businesses to sense, learn, respond, and evolve like a living organism, will be imperative for business excellence going forward. A comprehensive, yet modular suite of services is doing exactly that. Equipping organizations with intuitive decision-making automatically at scale, actionable insights based on real-time solutions, anytime/anywhere experience, and in-depth data visibility across functions leading to hyper-productivity, Live Enterprise is building connected organizations that are innovating collaboratively for the future.