Financial Services
How technology can drive value in the asset management landscape
Managing growth effectively is the need of the hour for most asset management technology firms. Professionally managed assets have grown globally, bringing with them new challenges.
- The changing regulatory landscape requires firms to comply with regulations such as Dodd-Frank and cost basis reporting in the US, and MiFID and AFIM in Europe.
- Reduction in traditional fee-based income has led asset managers to increase focus on non-core operations requiring a transformation in technology.
- Asset management firms need to scale up and amend their operating models across geographies to suit unique client requirements. They are required to streamline operations, drive down costs, and manage risks effectively.
Traditional asset management practices and labour-intensive models have been slow in adopting new technologies. They have emphasized on sales and growth over customer experience and retention.
Changing social and environmental trends have led buyers to prefer continuous relationships to transactional relationships with investment firms. However, most investment firms have failed to keep pace. Instead of being proactive, they have been reactive.
Although the number of sales professionals has increased, their individual profitability has declined. Discussions have revolved around pre-packaged products, and post-sale client communication has been mostly reactive.
“Asset managers must stay abreast of evolving demands on their business operating model, tech workforce, and the ability to drive sustainable change quickly.”
Three game-changers in financial asset management
1. Evolving buyers
Both individual and institutional buyers have evolved to become more complex, informed, demanding, diverse, and short on time. Optimal interaction between buyers and asset managers focuses on the following.
-
Content tailored to needs:
Asset managers get the attention of the buyers by engaging them with content tailored to their needs. Technology plays a big role in going beyond the superficial and grasping the real needs of each buyer. -
Thorough solutions:
After the first contact, buyers expect asset managers to hold detailed discussions and present customized solutions. -
Hassle-free processes:
Once the discussions mature and the buyers decide to purchase the product, they expect a flawless, automated, and technology-driven on-boarding process. -
Hassle-free processes:
Once the discussions mature and the buyers decide to purchase the product, they expect a flawless, automated, and technology-driven on-boarding process. -
Dedicated expertise:
Experienced asset managers bring in specialists to further understand the buyers’ needs and help them reach their financial goals.
2. Distribution economics
Asset managers have, for long, sensed the gap in distribution economics. To fill this gap, they have traditionally relied on hiring new salespeople. But this strategy has skyrocketed costs and brought down the profits without any significant results. Asset managers need helpful technology at the heart of their asset management strategy. Leveraging the power of such technology can deliver the following benefits.
-
Provide a single view of fragmented data:
Dashboards and breakthrough reporting tools can help consolidate data collected in an organization at different levels and geographies. An end-to-end view of an organization’s data is crucial. -
Convert raw data into useful information:
The management can easily transform raw data collected from different levels into valuable information that can be analysed to enable better decision-making. -
Streamline data flow:
Different tools are used in silos across the organization, causing data inconsistency, poor buyer experience, and increased costs. Technology can help streamline this inconsistency to transform the client’s buying journey. -
Create operating models that are a ‘right fit’ for asset managers:
These include lift and shift, utility models with gain share, and assisted captive models. The new operating model needs to be agile enough to differentiate between activities that add value and those that don’t.
3. Asset management technology and expertise
With increasing compliance requirements and client expectations, and reduced margins, technologies such as robotic process automation (RPA), artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and analytics will play a crucial role in the future of asset management.
Asset managers can adopt new distribution technologies for greater efficiency in acquiring and retaining new business. Enterprise-wide implementation of asset management technology, along with strategic investments in data analytics and client experience applications, can help:
- Remove intermediaries
- Compress value chains
- Reduce operating costs
- Boost efficiency
- Provide personalized services tailored to each customer’s needs
- Transform transactions into relationships by focusing on the buying experience of the client
For instance, data transformation programs for MiFID II compliance remove reliance on fragmented data and pushed firms towards retrievable, resilient, unified and elastic solutions. They also help improve investor protection by boosting transparency through regulatory reporting and tests.
OEMS, a workflow management tool developed by Infosys BPM for asset management functions, has benefited investment and retail banks. Similarly, FinRecon is a cost-effective reconciliation platform that helps automate workflow and reduce the associated effort and risk.
Asset management technology solutions for capital market transformation should cover the following key areas:
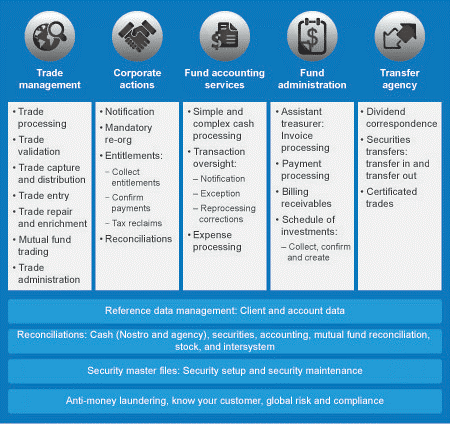
Continued acceptance of new processes across the organization needs the vision and direction of the leadership, a robust implementation plan, and strategic use of financial asset management services that can meet current gaps.
A seasoned, external perspective of the business, market, and industry can be a valuable ingredient in asset management transformation. It helps companies partner with consultants who have worked closely with asset managers, and who understand the operational dynamics, complexities of processes, and the market itself. Asset management solutions must also be combined with a talent pool trained in domain competency levels, latest technology, and processes.
Conclusion
Technology, when used right, can help asset managers understand their customers’ actual needs. They can unearth behavioural patterns using insights obtained from customer interests and transactions. This can help in providing personalized experiences in ways that were not possible before, and deliver tangible results in the ever-changing asset management landscape.
“Asset management firms need to promote a culture of innovation and incremental delivery now.”
Investing in more human capital can no longer help asset management firms meet the challenges of the future.
Combining focused implementation and continuous innovation is the only way to stay ahead of the competition, reduce capital and operational costs, and provide extraordinary buyer experience. Asset management firms must be iterative and agile, and need to evolve and adapt today for long-term sustainability.